On this page, I will post short summaries to a few of the projects I have completed while at Atlas that I am most proud of. These projects were completed in the specialization of Machine Learning. I think this will help showcase the Atlas Mantra of “Learn by doing” but also help educate others on what my capabilities are. To access the full list of projects in addition to the ones explained below, my github can be found here.
WURDO
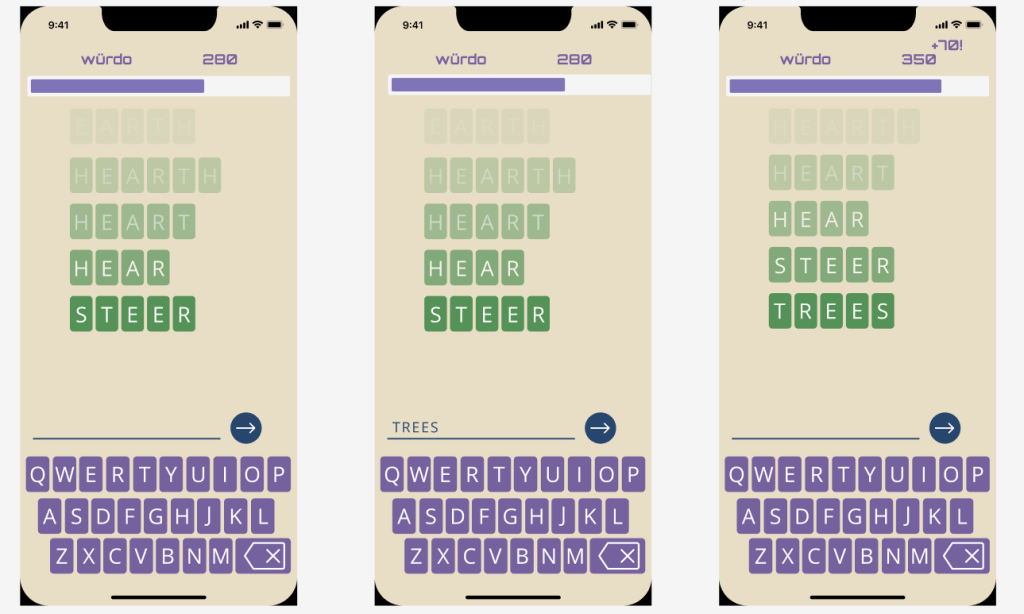
Würdo offers players a unique blend of classic word game mechanics and modern AI. A user begins with a randomly supplied word and must transform it into another valid word by changing, adding, or removing a single letter, creating an anagram, or finding a rhyme. The game’s ML model, a fine-tuned version of GPT-2, analyzes the semantic and contextual relationship between the words to generate a “creativity score.” This score, along with points for word length and transformation type, determines the final score. Players can choose a simple game mode or a more advanced tutorial where an AI companion, Umi, offers suggestions and plays alongside them.
Knight Runner
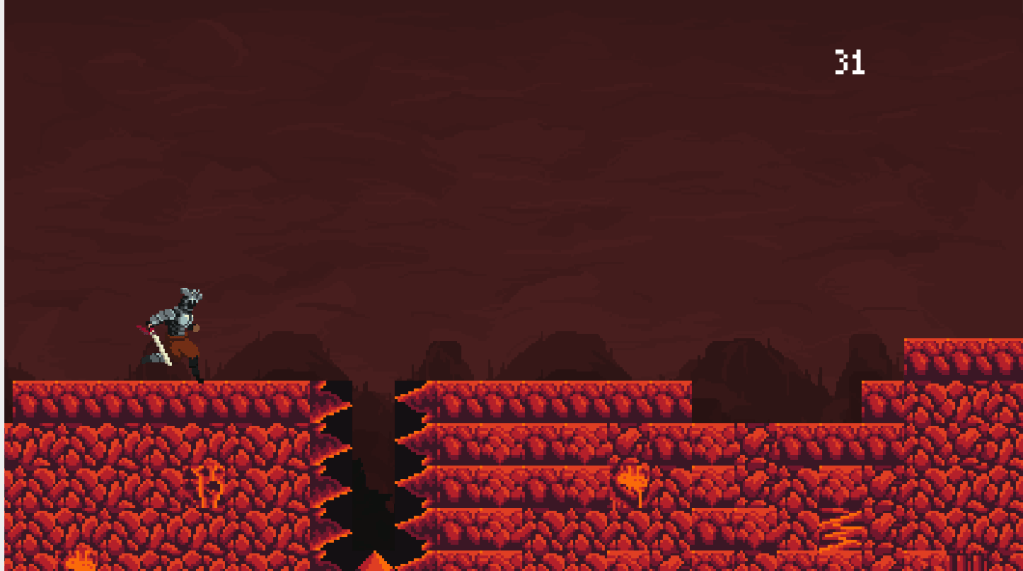

This screenshot comes from a game made as a team effort as part of a weeklong hacksprint. We decided to make a game in Godot and called it Knight Runner. It was an endless runner inspired by Googles dinosaur endless runner. We were able to build environments and animations as well as a score counter with a fully functioning main menu and pixel perfect collision detection. README
Classification Using neural networks
Neural Networks are quickly becoming some of the most important tools of a machine learning specialist that are meant to mimic the way the human brain works. Classification is a way of sifting through data and assigning labels to data points so that a person can look at it and know about certain relationships between data points or patterns. Classification systems have a wide range of applications like for use in self driving cars or facial recognition software. That was the first foray into classification that I made. README
Deep Convolutional Architectures
Neural Networks have different layers of complexity. Sometimes they are simple with a few inputs and a few layers leading to a few outputs. Sometimes however you need hundreds of layers with varying input, outputs with complext activation functions that take on massive amounts of processing power. CNN’s or convolutional neural networks are the most accurate tool for indentifying images. Like in facial recognition a deep CNN can identify the shape of a face in an image and hone on it and run it against a database to determinine if it has seen it before or not. creating a deep CNN is something that in the future will be a quickly growing tool for all sorts of technologies relying on something called computer vision. README
Object Detection using Computer Vision
Computer vision is basically concerning the way in which a computer is capable of interacting with data presented in a visual format. Object detection is training a neural network to identify and hone in on objects in a picture and identify those objects using common identifiable traits among them from a list of objects we gave to the network. For example it could differntiate between a bicycle and an automobile. Or a person and a cat or dog. It can still make mistakes which we had to be aware of.README
Optimization and Error Analysis of Neural Networks
Error analysis is a very important part of supervised learning. For instance, if you were trying to address a health condition like COVID and was using a testing network that provided false negatives (telling someone they werent infected when they were), the results could be disastrous. That is an extreme example, but shows how important it is to limit errors in neural networks and how optimization can combat the danger.README
Transfer Learning
Transfer Learning is a very simple concept. It is taking learning that was done by a certain neural network that worked on something similar. For instance we were trying to use transfer learing on the CIFAR-10 dataset which is 65k images by using learning done by a netwokr that had worked on a dataset of many millions of images called ImageNet. So we took some layers from the neural network and “froze” them so that they would do the same thing to our dataset that they did for the one in which they were previously used. Transfer Learning is very important and will grow in importance only being constrained by the amount of data it can be fed. README
